Zero-knowledge proofs are revolutionising blockchain. The two major standards SNARKs and STARKs are competing with each other, offering diverse scaling possibilities. However, everything comes at a price.
Zero-knowledge proofs, explained in detail in my previous publication, may eliminate the infamous blockchain scalability problem once and for all. Their properties allow us to offload the network and achieve higher transaction throughput.
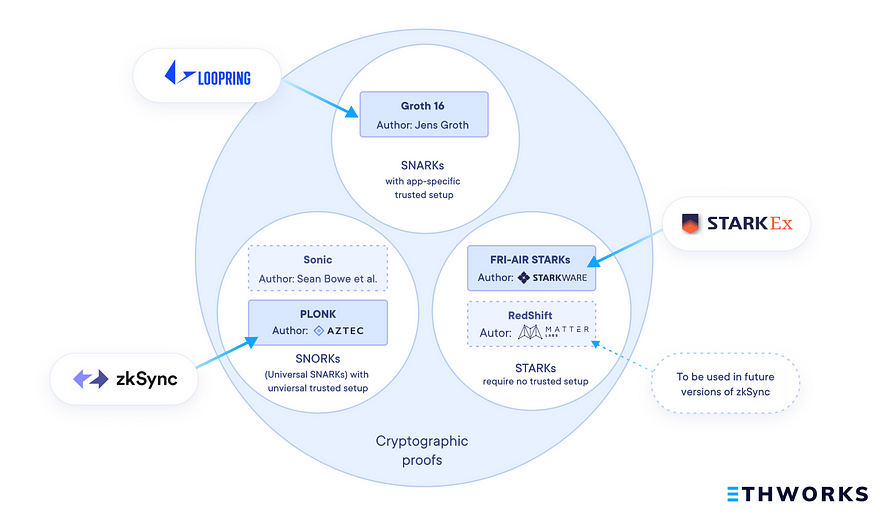
Several startups are already building scalability solutions using ZK cryptography. You may have heard about zkSync, loopring.io or StarkEx—their teams have announced their milestones recently, giving rise to a hot scalability debate.
Although all of these projects apply ZK cryptography, they utilise diverse types of zero-knowledge proofs. The logic behind them is equal, but technical details differ. Consequently, some of them allow for higher scalability but always at a cost.
Before diving deep, let’s start with the basics.
SNARKs and STARKs: Decoding the Names
You may wonder what these enigmatic names mean. Actually, they’re acronyms describing their properties.
As SNARK proofs appeared first, let’s begin with them. SNARK stands for:
- succinct: the proof is significantly smaller than the data it represents and can be verified quickly,
- non-interactive: only one set of information is sent by the prover to the verifier, thus there’s no back and forth interaction between them,
- argument of knowledge: the proof is considered computationally sound (a malicious prover isn’t likely to cheat the system without possessing the knowledge to support its statement).
The T present in the STARK name stands for transparent. It replaces the non-interactive property, which is what makes the biggest difference between SNARKs and STARKs. Translating the cryptographic jargon into English, STARKs, unlike SNARKs, don’t require trusted setup.
SNARKs: the Importance of Trusted Setup
Trusted setup, established between the prover and the verifier, is a set of initial public parameters that resemble the rules of a game. They’re generated during a so-called trusted setup ceremony: a joint computation performed in an arranged time by a group of voluntary participants.
As long as at least one of the parties behaves honestly, the parameters are generated securely. Thus, the teams using the SNARK standard encourage the general public to participate in their ceremonies to make them more “trusted”. Similarly, when a number of unrelated parties take part in them, the final products are considered more secure. All in all, with, say, 200 participants, a collusion is not likely to happen.
The typical SNARK proofs require conducting such a ceremony every time a new product version is launched. That’s how Loopring mentioned before works. However, there’s also a special type called universal trusted setup that allows reusing an ignition multi-party computing performed earlier. Thanks to that, there’s no need to conducting another ceremony when the zero-knowledge part of the protocol gets updates. Universal trusted setup is used in zkSync mentioned before.
STARKs: Another Level of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
STARKs, a new type of zero-knowledge proofs developed by StarkWare, don’t require trusted setup. This nuance makes them more secure as it eliminates the threat of initial collusion. Also, they make fewer cryptographic assumptions than SNARKs, which makes them harder to break. It might become important in the future since researchers suspect quantum computers could be a threat to SNARK security.
STARKs are generated faster, but they take up significantly more space, and so, more time is needed to verify them. Nonetheless, the amortised computation cost is still lower for big transaction batches (that are the foundation of ZK-based scalability solutions; read more here). Therefore, they allow us to achieve higher scalability.
STARKs are currently used by StarkEx and its complementary protocol StarkPay. However, as they scale blockchains more effectively, probably more companies will be interested in applying them. zkSync creators are already planning to switch to them.

The Future of Blockchain Scaling
As scalability is the major blocker preventing blockchains from mass adoption, we’ll probably see more research on zero-knowledge proofs in the future. We may expect more standards to emerge, and let’s face it: it’s an exciting perspective!
Want to know more about the use of zero-knowledge cryptography for scaling blockchains? Or the products mentioned in my article? Ethworks described it in detail in its latest report: Zero-Knowledge Blockchain Scaling. In addition to easily-digestible explanations, it features beautiful illustrations facilitating understanding tough concepts. Check it out here!
Also Read




