This is my first major study (source) about Blockchain Interoperability, which started in December 2019 and was last updated today.
We analysed 330+ documents and obtained feedback from 30 people, to categorize the most relevant blockchain interoperability projects. We came up with three categories: Cryptocurrency-directed interoperability approaches, Blockchain Engines, and Blockchain Connectors.
Note: for an introduction on blockchain technology, the blockchain interoperability problem, and for a full discussion on each category, blockchain interoperability definitions, architectures for blockchain interoperability, existing standards, open issues and challenges, and use case scenarios, refer to the paper: A Survey on Blockchain Interoperability: Past, Present, and Future Trends.
General Overview:
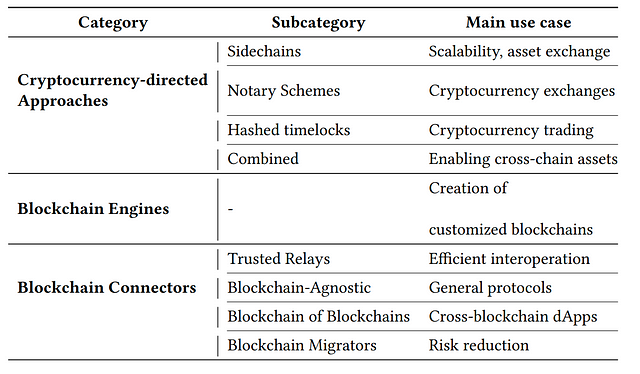

Three categories: Cryptocurrency-directed interoperability approaches, Blockchain Engines, and Blockchain Connectors. It is worth pointing out that most research available (especially Blockchain Connectors and recent updates from Blockchain Engines) are very recent (since 2017, being the majority dated from 2019).
1: Cryptocurrency-directed interoperability approaches
The paper states “In this category, we identify and define different strategies for chain interoperability across public blockchains, most of them implementing cryptocurrencies. The criteria that we used to classify each solution follows Buterin’s classification […] sidechain (or relay chain) approaches, notary schemes and timed hash-locks. This categorization considers only public blockchains, as at the time there were no private blockchains. We consider an additional category that we denominate combined solutions.
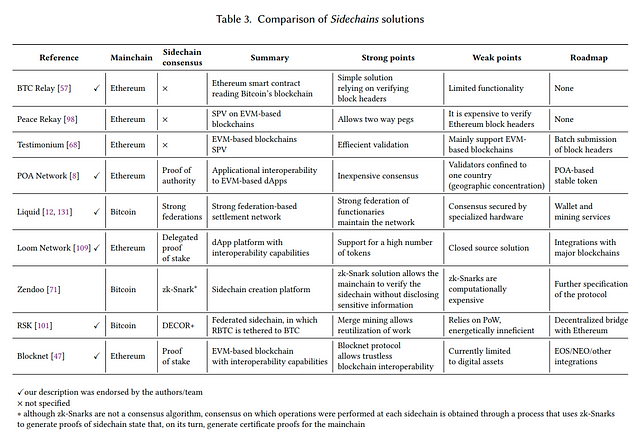
1.1 Sidechains
“A sidechain (or secondary chain, or relay chain) is a mechanism for two existing blockchains to interoperate, scale (e.g., via blockchain sharding), and be upgraded in which one blockchain (main chain or mainchain) considers another blockchain as an extension of itself (the sidechain)”.

1.2 Notary Schemes
“A notary is an entity that monitors multiple chains, triggering transactions in a chain upon an event (e.g., a smart contract being deployed) taking place on another chain”. Typical examples are centralized exchanges.
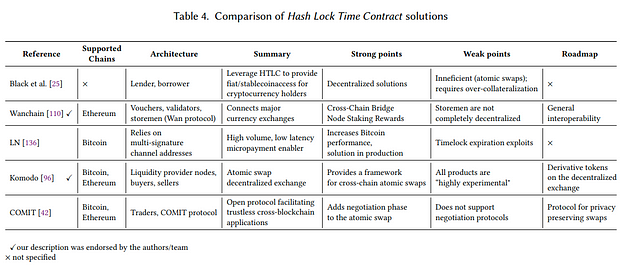
1.3 Hashed Time-Locks
“Hashed time-locks contracts (HTLCs) initially appeared as an alternative to centralized exchanges, as they enable cross-chain atomic operations. HTLCs techniques use hashlocks and timelocks to enforce atomicity of operations, normally between two parties”.

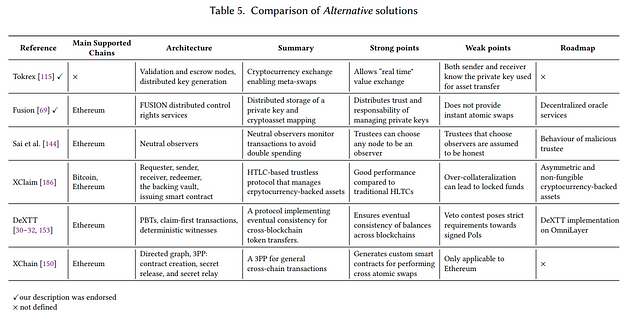
1.4 Combined Solutions
Cryptocurrency-directed interoperability approaches that do not fit on other sub-categories.

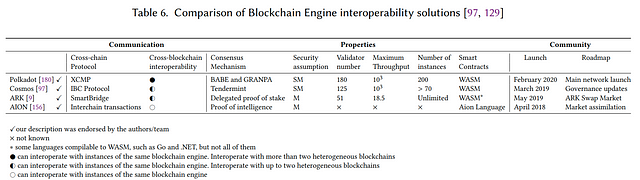
2. Blockchain Engines
“While the Cryptocurrency based interoperability approaches category focus on cryptocurrency ecosystems, mostly homogeneous blockchain systems, the present category focus on general use-cases and heterogeneous systems. We define Blockchain Engines as frameworks that provide reusable data, network, consensus, incentive, and contract layers for the creation of customized blockchains, to power decentralized applications, that interoperate between each other”.
The famous examples are the Cosmos Network and Polkadot.

3. Blockchain Connectors
“The Blockchain Connector category is composed of interoperability solutions that are not cryptocurrency-directed or blockchain engines. We remark the several sub-categories we derived from the studies available: Trusted Relays, Blockchain Agnostic Protocols, Blockchain of Blockchains, and Blockchain Migrators”.
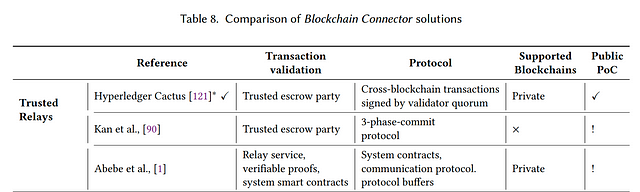
3.1 Trusted Relays
“Trusted relays are directed to environments where there is a blockchain registry facilitating the discovery of the target blockchains. Typically, such a scheme appears in a permissioned blockchain environment, where cross-blockchain transactions are routed by trusted escrow parties”.

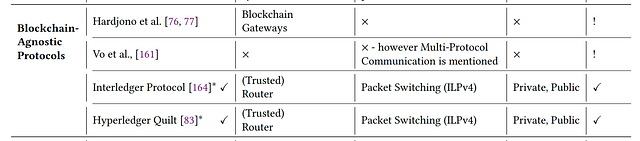
3.2 Blockchain-agnostic protocols
“As the name suggests, provide technology-agnostic protocols for interoperation between distributed ledger systems, but do not guarantee backwards compatibility. In other words, in order existing blockchains to use such protocols, their source code has to be changed”.

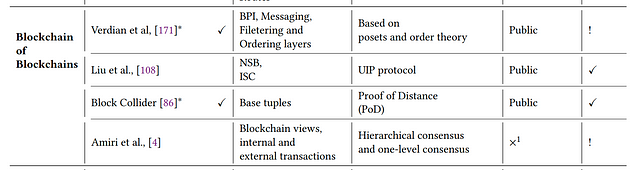
3.3 Blockchain of blockchains
Blockchain of blockchains provide mechanisms for developers to build cross-chain dApps.

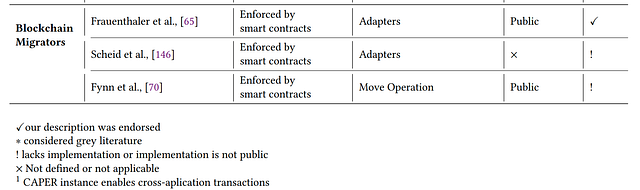
3.4 Blockchain migrators
Solutions that perform data migration across blockchains, which resemble notary schemes from the category 1.

Discussion:


If you are interested into the latest solutions, please refer to the paper. I would like to highlight Hyperledger Cactus, a very promising open-source project, in terms of blockchain interoperability experience. Cactus is the newest Hyperledger project (dated May 2020), which provides a great variety of use-cases, one of them blockchain migration. Although Cactus currently is a trusted relay, the source of trust can be changed (for example, trust is deposited into a blockchain-based application running on Ethereum).
Thanks for reading! This is a work in progress. Any comments or suggestions are greatly welcomed and they still can be incorporated.




